- Install NuGet
- Use the GitLab endpoint for NuGet Packages
- Add the Package Registry as a source for NuGet packages
- Publish a NuGet package
- Install packages
- Symbol packages
- Supported CLI commands
NuGet packages in the Package Registry
- Introduced in GitLab Premium 12.8.
- Moved to GitLab Free in 13.3.
- Symbol package support added in GitLab 14.1.
Publish NuGet packages in your project’s Package Registry. Then, install the packages whenever you need to use them as a dependency.
The Package Registry works with:
For documentation of the specific API endpoints that these clients use, see the NuGet API documentation.
Install NuGet
The required minimum versions are:
- NuGet CLI 5.1 or later. If you have Visual Studio, the NuGet CLI is probably already installed.
- Alternatively, you can use .NET SDK 3.0 or later, which installs the NuGet CLI.
- NuGet protocol version 3 or later.
Verify that the NuGet CLI is installed by running:
nuget help
The output should be similar to:
NuGet Version: 5.1.0.6013
usage: NuGet <command> [args] [options]
Type 'NuGet help <command>' for help on a specific command.
Available commands:
[output truncated]
Install NuGet on macOS
For macOS, you can use Mono to run the NuGet CLI.
- If you use Homebrew, to install Mono, run
brew install mono. - Download the Windows C# binary
nuget.exefrom the NuGet CLI page. -
Run this command:
mono nuget.exe
Use the GitLab endpoint for NuGet Packages
Introduced group-level endpoint in GitLab 13.8.
To use the GitLab endpoint for NuGet Packages, choose an option:
- Project-level: Use when you have few NuGet packages and they are not in the same GitLab group.
- Group-level: Use when you have many NuGet packages in different projects within the same GitLab group.
Some features such as publishing a package are only available on the project-level endpoint.
Add the Package Registry as a source for NuGet packages
To publish and install packages to the Package Registry, you must add the Package Registry as a source for your packages.
Prerequisites:
- Your GitLab username.
- A personal access token or deploy token. For repository authentication:
- You can generate a personal access token
with the scope set to
api. - You can generate a deploy token
with the scope set to
read_package_registry,write_package_registry, or both.
- You can generate a personal access token
with the scope set to
- A name for your source.
- Depending on the endpoint level you use, either:
- Your project ID, which is found on your project’s home page.
- Your group ID, which is found on your group’s home page.
You can now add a new source to NuGet with:
Add a source with the NuGet CLI
Project-level endpoint
A project-level endpoint is required to publish NuGet packages to the Package Registry. A project-level endpoint is also required to install NuGet packages from a project.
To use the project-level NuGet endpoint, add the Package Registry as a source with nuget:
nuget source Add -Name <source_name> -Source "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<your_project_id>/packages/nuget/index.json" -UserName <gitlab_username or deploy_token_username> -Password <gitlab_personal_access_token or deploy_token>
-
<source_name>is the desired source name.
For example:
nuget source Add -Name "GitLab" -Source "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/10/packages/nuget/index.json" -UserName carol -Password 12345678asdf
Group-level endpoint
To install a NuGet package from a group, use a group-level endpoint.
To use the group-level NuGet endpoint, add the Package Registry as a source with nuget:
nuget source Add -Name <source_name> -Source "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/groups/<your_group_id>/-/packages/nuget/index.json" -UserName <gitlab_username or deploy_token_username> -Password <gitlab_personal_access_token or deploy_token>
-
<source_name>is the desired source name.
For example:
nuget source Add -Name "GitLab" -Source "https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/groups/23/-/packages/nuget/index.json" -UserName carol -Password 12345678asdf
Add a source with Visual Studio
Project-level endpoint
A project-level endpoint is required to publish NuGet packages to the Package Registry. A project-level endpoint is also required to install NuGet packages from a project.
To use the project-level NuGet endpoint, add the Package Registry as a source with Visual Studio:
- Open Visual Studio.
- In Windows, select File > Options. On macOS, select Visual Studio > Preferences.
- In the NuGet section, select Sources to view a list of all your NuGet sources.
- Select Add.
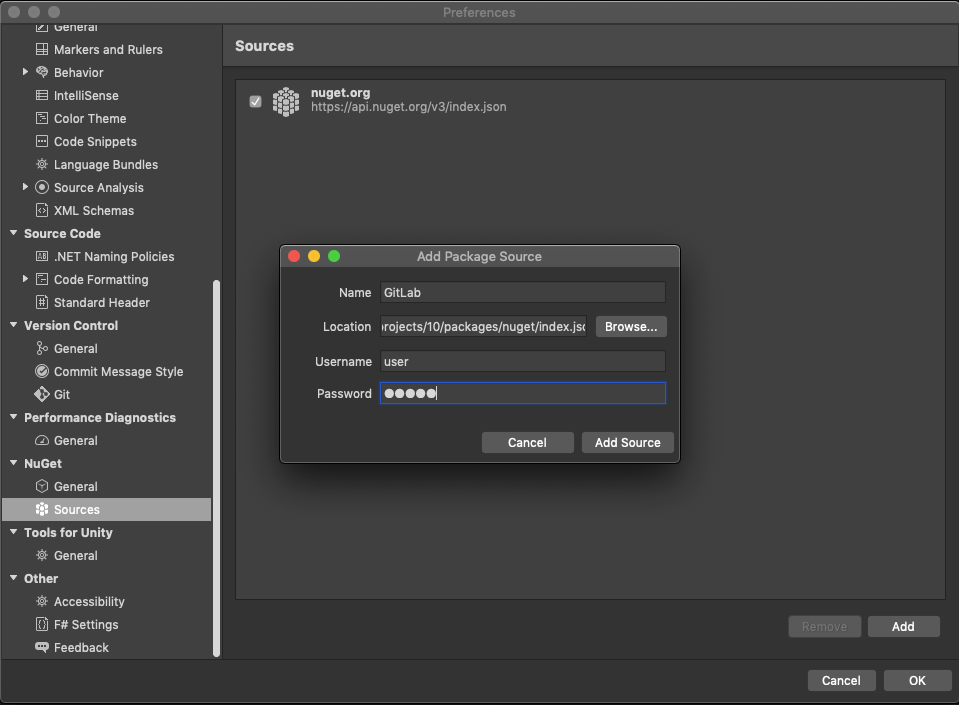
- Complete the following fields:
- Name: Name for the source.
-
Location:
https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<your_project_id>/packages/nuget/index.json, where<your_project_id>is your project ID, andgitlab.example.comis your domain name. - Username: Your GitLab username or deploy token username.
- Password: Your personal access token or deploy token.
- Click Save.
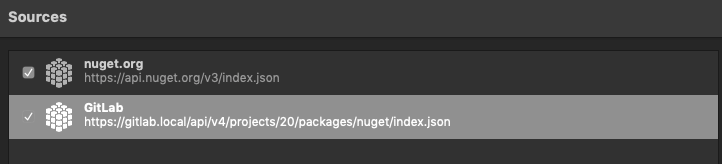
The source is displayed in your list.
If you get a warning, ensure that the Location, Username, and Password are correct.
Group-level endpoint
To install a package from a group, use a group-level endpoint.
To use the group-level NuGet endpoint, add the Package Registry as a source with Visual Studio:
- Open Visual Studio.
- In Windows, select File > Options. On macOS, select Visual Studio > Preferences.
- In the NuGet section, select Sources to view a list of all your NuGet sources.
- Select Add.
- Complete the following fields:
- Name: Name for the source.
-
Location:
https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/groups/<your_group_id>/-/packages/nuget/index.json, where<your_group_id>is your group ID, andgitlab.example.comis your domain name. - Username: Your GitLab username or deploy token username.
- Password: Your personal access token or deploy token.
- Click Save.
The source is displayed in your list.
If you get a warning, ensure that the Location, Username, and Password are correct.
Add a source with the .NET CLI
Project-level endpoint
A project-level endpoint is required to publish NuGet packages to the Package Registry. A project-level endpoint is also required to install NuGet packages from a project.
To use the project-level Package Registry as a source for .NET:
- In the root of your project, create a file named
nuget.config. -
Add this content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <packageSources> <clear /> <add key="gitlab" value="https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/<your_project_id>/packages/nuget/index.json" /> </packageSources> <packageSourceCredentials> <gitlab> <add key="Username" value="<gitlab_username or deploy_token_username>" /> <add key="ClearTextPassword" value="<gitlab_personal_access_token or deploy_token>" /> </gitlab> </packageSourceCredentials> </configuration>
Group-level endpoint
To install a package from a group, use a group-level endpoint.
To use the group-level Package Registry as a source for .NET:
- In the root of your project, create a file named
nuget.config. -
Add this content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <packageSources> <clear /> <add key="gitlab" value="https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/groups/<your_group_id>/-/packages/nuget/index.json" /> </packageSources> <packageSourceCredentials> <gitlab> <add key="Username" value="<gitlab_username or deploy_token_username>" /> <add key="ClearTextPassword" value="<gitlab_personal_access_token or deploy_token>" /> </gitlab> </packageSourceCredentials> </configuration>
Publish a NuGet package
Prerequisite:
- Set up the source with a project-level endpoint.
When publishing packages:
- The Package Registry on GitLab.com can store up to 5 GB of content. This limit is configurable for self-managed GitLab instances.
- If you publish the same package with the same version multiple times, each consecutive upload is saved as a separate file. When installing a package, GitLab serves the most recent file.
- When publishing packages to GitLab, they aren’t displayed in the packages user interface of your project immediately. It can take up to 10 minutes to process a package.
Publish a package with the NuGet CLI
Prerequisites:
Publish a package by running this command:
nuget push <package_file> -Source <source_name>
-
<package_file>is your package filename, ending in.nupkg. -
<source_name>is the source name used during setup.
Publish a package with the .NET CLI
Prerequisites:
Publish a package by running this command:
dotnet nuget push <package_file> --source <source_name>
-
<package_file>is your package filename, ending in.nupkg. -
<source_name>is the source name used during setup.
For example:
dotnet nuget push MyPackage.1.0.0.nupkg --source gitlab
Publish a NuGet package by using CI/CD
Introduced in GitLab 13.3.
If you’re using NuGet with GitLab CI/CD, a CI job token can be used instead of a personal access token or deploy token. The token inherits the permissions of the user that generates the pipeline.
This example shows how to create a new package each time the master branch is
updated:
-
Add a
deployjob to your.gitlab-ci.ymlfile:image: mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/sdk:3.1 stages: - deploy deploy: stage: deploy script: - dotnet pack -c Release - dotnet nuget add source "${CI_API_V4_URL}/${CI_PROJECT_ID}/packages/nuget/index.json" --name gitlab --username gitlab-ci-token --password $CI_JOB_TOKEN --store-password-in-clear-text - dotnet nuget push "bin/Release/*.nupkg" --source gitlab only: - master -
Commit the changes and push it to your GitLab repository to trigger a new CI/CD build.
Publishing a package with the same name or version
When you publish a package with the same name or version as an existing package, the existing package is overwritten.
Install packages
To install a NuGet package from the Package Registry, you must first add a project-level or group-level endpoint.
If multiple packages have the same name and version, when you install a package, the most recently-published package is retrieved.
Install a package with the NuGet CLI
nuget checks the official source at nuget.org first. If you have
a NuGet package in the Package Registry with the same name as a package at
nuget.org, you must specify the source name to install the correct package.Install the latest version of a package by running this command:
nuget install <package_id> -OutputDirectory <output_directory> \
-Version <package_version> \
-Source <source_name>
-
<package_id>is the package ID. -
<output_directory>is the output directory, where the package is installed. -
<package_version>The package version. Optional. -
<source_name>The source name. Optional.
Install a package with the .NET CLI
dotnet checks sources during
install. This is defined in the nuget.config file.Install the latest version of a package by running this command:
dotnet add package <package_id> \
-v <package_version>
-
<package_id>is the package ID. -
<package_version>is the package version. Optional.
Symbol packages
Introduced in GitLab 14.1.
If you push a .nupkg, symbol package files in the .snupkg format are uploaded automatically. You
can also push them manually:
nuget push My.Package.snupkg -Source <source_name>
Consuming symbol packages is not yet guaranteed using clients such as Visual Studio or
dotnet-symbol. The .snupkg files are available for download through the UI or the
API.
Follow the NuGet symbol package issue for further updates.
Supported CLI commands
The GitLab NuGet repository supports the following commands for the NuGet CLI (nuget) and the .NET
CLI (dotnet):
-
nuget push: Upload a package to the registry. -
dotnet nuget push: Upload a package to the registry. -
nuget install: Install a package from the registry. -
dotnet add: Install a package from the registry.