- Add an existing EKS cluster
- Create a new certificate-based EKS cluster
- Create a default Storage Class
- Deploy the app to EKS
- Additional requirements for self-managed instances
- Troubleshooting
EKS clusters (DEPRECATED)
- Introduced in GitLab 12.5.
- Deprecated in GitLab 14.0.
Through GitLab, you can create new clusters and add existing clusters hosted on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
Add an existing EKS cluster
If you already have an EKS cluster and want to integrate it with GitLab, see how to add an existing cluster.
Create a new certificate-based EKS cluster
Prerequisites:
- An Amazon Web Services account.
- Permissions to manage IAM resources.
For instance-level clusters, see additional requirements for self-managed instances.
To create new Kubernetes clusters for your project, group, or instance through the certificate-based method:
- Define the access control (RBAC or ABAC) for your cluster.
- Create a cluster in GitLab.
- Prepare the cluster in Amazon.
- Configure your cluster’s data in GitLab.
Further steps:
Create a new EKS cluster in GitLab
To create a new EKS cluster:
- Go to your:
- Project’s Infrastructure > Kubernetes clusters page, for a project-level cluster.
- Group’s Kubernetes page, for a group-level cluster.
- Menu > Admin > Kubernetes, for an instance-level cluster.
- Select Integrate with a cluster certificate.
- Under the Create new cluster tab, click Amazon EKS to display an
Account IDandExternal IDneeded for later steps. - In the IAM Management Console, create an IAM policy:
- From the left panel, select Policies.
- Select Create Policy, which opens a new window.
-
Select the JSON tab, and paste the following snippet in place of the existing content. These permissions give GitLab the ability to create resources, but not delete them:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "autoscaling:CreateAutoScalingGroup", "autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups", "autoscaling:DescribeScalingActivities", "autoscaling:UpdateAutoScalingGroup", "autoscaling:CreateLaunchConfiguration", "autoscaling:DescribeLaunchConfigurations", "cloudformation:CreateStack", "cloudformation:DescribeStacks", "ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress", "ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress", "ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupEgress", "ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupIngress", "ec2:CreateSecurityGroup", "ec2:createTags", "ec2:DescribeImages", "ec2:DescribeKeyPairs", "ec2:DescribeRegions", "ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups", "ec2:DescribeSubnets", "ec2:DescribeVpcs", "eks:CreateCluster", "eks:DescribeCluster", "iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile", "iam:AttachRolePolicy", "iam:CreateRole", "iam:CreateInstanceProfile", "iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole", "iam:GetRole", "iam:listAttachedRolePolicies", "iam:ListRoles", "iam:PassRole", "ssm:GetParameters" ], "Resource": "*" } ] }If you get an error during this process, GitLab does not roll back the changes. You must remove resources manually. You can do this by deleting the relevant CloudFormation stack.
- Click Review policy.
- Enter a suitable name for this policy, and click Create Policy. You can now close this window.
Prepare the cluster in Amazon
- Create an EKS IAM role for your cluster (role A).
- Create another EKS IAM role for GitLab authentication with Amazon (role B).
Create an EKS IAM role for your cluster
In the IAM Management Console, create an EKS IAM role (role A) following the Amazon EKS cluster IAM role instructions. This role is necessary so that Kubernetes clusters managed by Amazon EKS can make calls to other AWS services on your behalf to manage the resources that you use with the service.
For GitLab to manage the EKS cluster correctly, you must include AmazonEKSClusterPolicy in
addition to the policies the guide suggests.
Create another EKS IAM role for GitLab authentication with Amazon
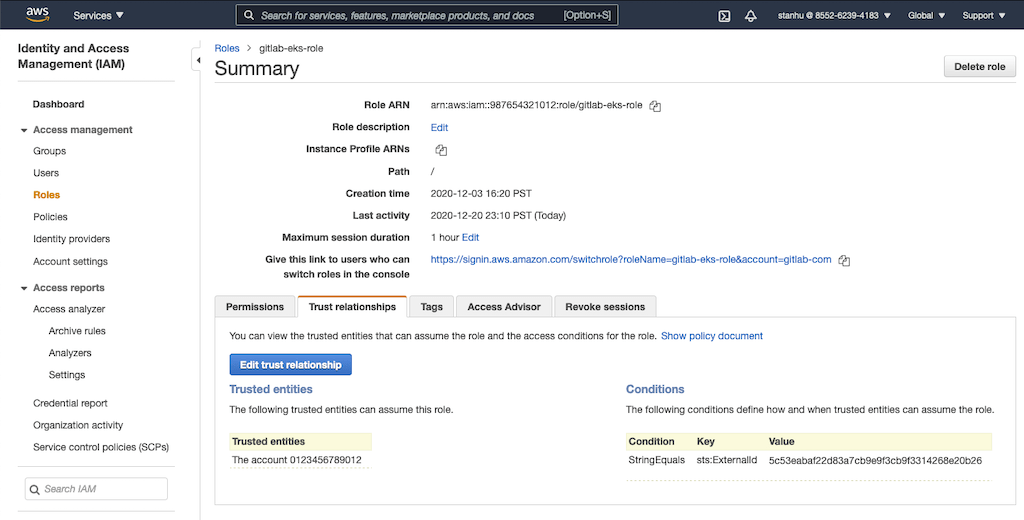
In the IAM Management Console, create another IAM role (role B) for GitLab authentication with AWS:
- On the AWS IAM console, select Roles from the left panel.
- Click Create role.
- Under Select type of trusted entity, select Another AWS account.
- Enter the Account ID from GitLab into the Account ID field.
- Check Require external ID.
- Enter the External ID from GitLab into the External ID field.
- Click Next: Permissions, and select the policy you just created.
- Click Next: Tags, and optionally enter any tags you wish to associate with this role.
- Click Next: Review.
- Enter a role name and optional description into the fields provided.
- Click Create role. The new role name displays at the top. Click on its name and copy the
Role ARNfrom the newly created role.
Configure your cluster’s data in GitLab
- Back in GitLab, enter the copied role ARN into the Role ARN field.
- In the Cluster Region field, enter the region you plan to use for your new cluster. GitLab confirms you have access to this region when authenticating your role.
- Select Authenticate with AWS.
- Adjust your cluster’s settings.
- Select the Create Kubernetes cluster button.
After about 10 minutes, your cluster is ready to go.
kubectl and you would like to manage your cluster with it, you must add your AWS external ID in the AWS configuration. For more information on how to configure AWS CLI, see using an IAM role in the AWS CLI.Cluster settings
When you create a new cluster, you have the following settings:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes cluster name | Your cluster’s name. |
| Environment scope | The associated environment. |
| Service role | The EKS IAM role (role A). |
| Kubernetes version | The Kubernetes version for your cluster. |
| Key pair name | The key pair that you can use to connect to your worker nodes. |
| VPC | The VPC to use for your EKS Cluster resources. |
| Subnets | The subnets in your VPC where your worker nodes run. Two are required. |
| Security group | The security group to apply to the EKS-managed Elastic Network Interfaces that are created in your worker node subnets. |
| Instance type | The instance type of your worker nodes. |
| Node count | The number of worker nodes. |
| GitLab-managed cluster | Check if you want GitLab to manage namespaces and service accounts for this cluster. |
Create a default Storage Class
Amazon EKS doesn’t have a default Storage Class out of the box, which means requests for persistent volumes are not automatically fulfilled. As part of Auto DevOps, the deployed PostgreSQL instance requests persistent storage, and without a default storage class it cannot start.
If a default Storage Class doesn’t already exist and is desired, follow Amazon’s guide on storage classes to create one.
Alternatively, disable PostgreSQL by setting the project variable
POSTGRES_ENABLED to false.
Deploy the app to EKS
With RBAC disabled and services deployed, Auto DevOps can now be leveraged to build, test, and deploy the app.
Enable Auto DevOps
if not already enabled. If a wildcard DNS entry was created resolving to the
Load Balancer, enter it in the domain field under the Auto DevOps settings.
Otherwise, the deployed app isn’t externally available outside of the cluster.
GitLab creates a new pipeline, which begins to build, test, and deploy the app.
After the pipeline has finished, your app runs in EKS, and is available to users. Click on CI/CD > Environments.
GitLab displays a list of the environments and their deploy status, as well as options to browse to the app, view monitoring metrics, and even access a shell on the running pod.
Additional requirements for self-managed instances
If you are using a self-managed GitLab instance, you need to configure Amazon credentials. GitLab uses these credentials to assume an Amazon IAM role to create your cluster.
Create an IAM user and ensure it has permissions to assume the role(s) that your users need to create EKS clusters.
For example, the following policy document allows assuming a role whose name starts with
gitlab-eks- in account 123456789012:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": {
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/gitlab-eks-*"
}
}
Configure Amazon authentication
To configure Amazon authentication in GitLab, generate an access key for the IAM user in the Amazon AWS console, and follow these steps:
- In GitLab, on the top bar, select Menu > Admin > Settings > General and expand the Amazon EKS section.
- Check Enable Amazon EKS integration.
- Enter your Account ID.
- Enter your access key and ID.
- Click Save changes.
EKS access key and ID
Instance profiles were introduced in GitLab 13.7.
If you’re using GitLab 13.7 or later, you can use instance profiles to
dynamically retrieve temporary credentials from AWS when needed.
In this case, leave the Access key ID and Secret access key fields blank
and pass an IAM role to an EC2 instance.
Otherwise, enter your access key credentials into Access key ID and Secret access key.
Troubleshooting
The following errors are commonly encountered when creating a new cluster.
Validation failed: Role ARN must be a valid Amazon Resource Name
Check that the Provision Role ARN is correct. An example of a valid ARN:
arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/gitlab-eks-provision'
Access denied: User arn:aws:iam::x is not authorized to perform: sts:AssumeRole on resource: arn:aws:iam::y
This error occurs when the credentials defined in the Configure Amazon authentication cannot assume the role defined by the Provision Role ARN. Check that:
- The initial set of AWS credentials has the AssumeRole policy.
- The Provision Role has access to create clusters in the given region.
-
The account ID and external ID match the value defined in the Trust relationships tab in AWS:
Could not load Security Groups for this VPC
When populating options in the configuration form, GitLab returns this error because GitLab has successfully assumed your provided role, but the role has insufficient permissions to retrieve the resources needed for the form. Make sure you’ve assigned the role the correct permissions.
Key Pairs are not loaded
GitLab loads the key pairs from the Cluster Region specified. Ensure that key pair exists in that region.
ROLLBACK_FAILED during cluster creation
The creation process halted because GitLab encountered an error when creating one or more resources. You can inspect the associated CloudFormation stack to find the specific resources that failed to create.
If the Cluster resource failed with the error
The provided role doesn't have the Amazon EKS Managed Policies associated with it.,
the role specified in Role name is not configured correctly.
AmazonEKSClusterPolicy policy for this role in order for GitLab to manage the EKS cluster correctly.